How to Get the Most Out of Our Model - SIMD-ai-2506.1:24b
This post is a follow-up to last week’s blog: Meet SIMD.ai – A Specialist LLM for SIMD Porting.
If you’ve already tested our model, this guide will help you get the best results from SIMD-ai-2506.1:24b—including prompting tips, best practices, and details on new API access (generate an API key in your account and check your dashboard to get started with integration).
🧪 Heads up: SIMD-ai-2506.1:24b is still in beta. It works well, but you might run into occasional hiccups — we’re refining it constantly.
Supported SIMD Engines
As mentioned in our previous blog, the model currently supports the following SIMD engines:
- SSE4.2
- NEON
- VSX
For this first release, we’ve focused on 128-bit vector lengths, so output for other engines like AVX512 or SVE won’t be accurate — yet. Support for more architectures is on the roadmap, and we’ll post updates as they roll out.
Also worth noting: the model hasn’t been trained on Scalar-to-SIMD translation. It’s optimized specifically for SIMD-to-SIMD porting between the supported backends. Stick to that for now to get the best results.
Model's Translation Capabilities
SIMD-ai-2506.1:24b has been fine-tuned specifically for two core SIMD translation tasks:
Intrinsic-to-Intrinsic Mapping
Got a codebase using SSE4.2 and need to port it to NEON or VSX? This model can do that — it maps intrinsics accurately and consistently between supported architectures.
And we’re not just saying that. We built LLaMeSIMD, the first-ever benchmarking suite for evaluating how well LLMs can translate between SIMD instruction sets. You can run it yourself and see how our model stacks up.Function-Level Translation
Want to port an entire function? No problem. The model performs best on functions roughly 10–15 lines long. For longer functions, we recommend breaking them into smaller logical parts for better results.
Keep in mind, some intrinsics don’t have direct 1:1 equivalents across all architectures. In those cases, the model may generate equivalent behavior using multiple intrinsics — but results can vary. We're working on improving this in future updates.
Prompting Tips & Best Practices
After testing over 50 open-source models and many top proprietary ones (check out the benchmarks in our previous posts: Leveraging LLMs for SIMD Optimization and DeepSeek-R1 Meets SIMD Code Porting), we’ve learned a lot about what makes prompts work — and what doesn’t.
Based on all that testing, plus countless hours working with SIMD-ai-2506.1:24b, here are some practical tips to get the most accurate and useful results from the model:
Be explicit about source and target architectures
Always mention both the source and target SIMD engines in your prompt. This is critical for both intrinsic-level and function-level translations.Prompting for Intrinsic-to-Intrinsic Mapping
Use a clear and direct format like:Can you give me the equivalent intrinsic of "_mm_add_ps" from engine SSE4.2 to engine NEON?Prompting for Function-Level Translation
When translating full functions, structure your prompt like:I have a function written using SSE4.2 intrinsics and I want to translate it to NEON. Can you help?Keep function size reasonable
As mentioned earlier, the model performs best on functions that are roughly 10–15 lines long. For longer code, break it down into smaller, logically separated chunks before translating.Add a fallback instruction for edge cases
Append this sentence to your prompt for more robust results:If there is no direct equivalent intrinsic in the target architecture, try to replicate the behavior using multiple intrinsics instead of just one.Use external context when needed
If the model struggles to recognize or understand a particular intrinsic, add context to it from our our knowledge base simd.info.Don’t hesitate to iterate
If the output isn’t quite right, ask the model to try again and explain what was wrong. Often, a small clarification in your feedback can lead to much better results.
What the Model Can't Do (Yet)
While SIMD-ai-2506.1:24b is powerful, there are still some limits to keep in mind:
No Scalar-to-SIMD Translation
The model isn’t trained to convert scalar code into SIMD intrinsics yet. It’s focused solely on SIMD-to-SIMD porting.Limited Support for Wider Vectors
Currently, only 128-bit SIMD engines like SSE4.2, NEON, and VSX are supported. Wider vectors (e.g., AVX512, SVE) are not reliably translated yet.Long Functions Are Tricky
Functions longer than 15 lines often need to be broken into smaller parts for good results.
In these unsupported cases, the model will still generate an answer — but it likely won’t be valid or usable. We’re actively working on expanding capabilities and improving these areas in future updates. Now let's get to the API setup.
Using Continue with our SIMD.ai API Key
Continue is an open-source VS Code plugin that enables code suggestions using your own API key. This guide shows you how to set it up with your SIMD.ai API key.
- Install Continue in VS Code
- Open VS Code.
- Go to the Extensions Marketplace by clicking on the Extensions icon in the Activity Bar or pressing
Ctrl+Shift+X. - Search for "Continue" and install the extension.
- Configure Our Own Model
- Navigate to API Key Settings
- View More Providers
- Access the Config File
- In the settings or through the extension interface, find and click on the option to access the config file.
- Copy the Config File
Copy the provided
config.yamlfile.Navigate to the
.continue/directory of your project.Paste the
config.yamlfile into this directory.# .continue/config.yaml name: Local Assistant version: 1.0.0 schema: v1 models: - name: SIMD.ai provider: openai model: SIMD-ai-2506.1.ai:24b apiBase: https://simd.ai/api/ apiKey: YOUR-API-KEY roles: - chat capabilities: - tool_use context: - provider: code - provider: docs - provider: diff - provider: terminal - provider: problems - provider: folder - provider: codebaseNote: Default parameters and context size are currently ignored — we use our own internal configuration.
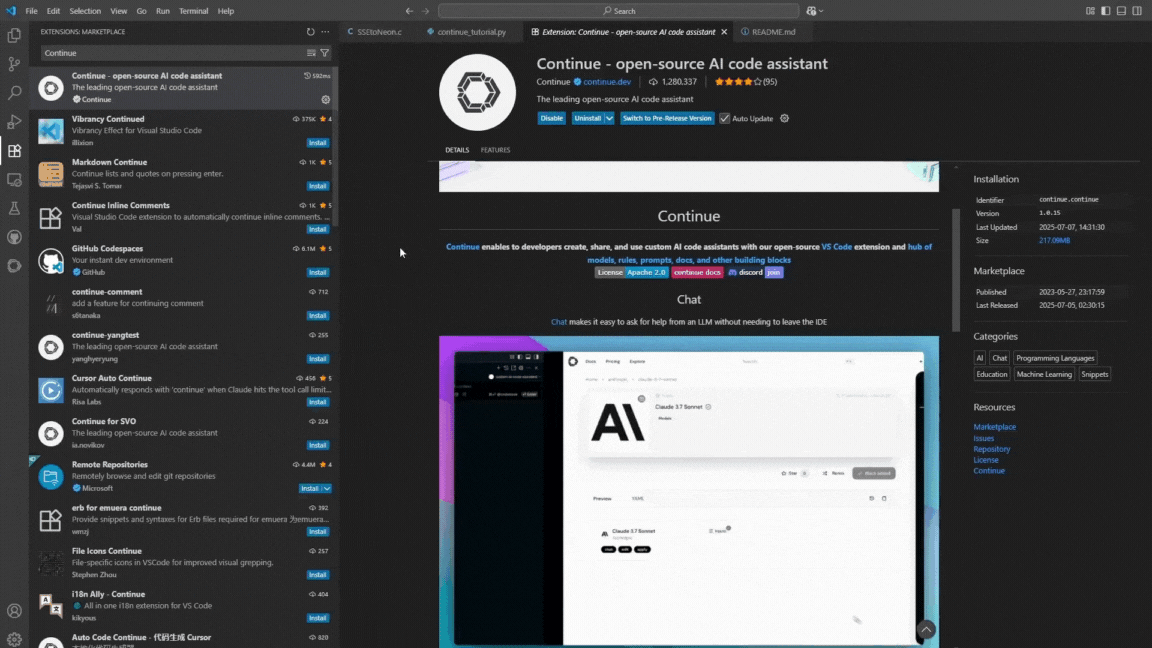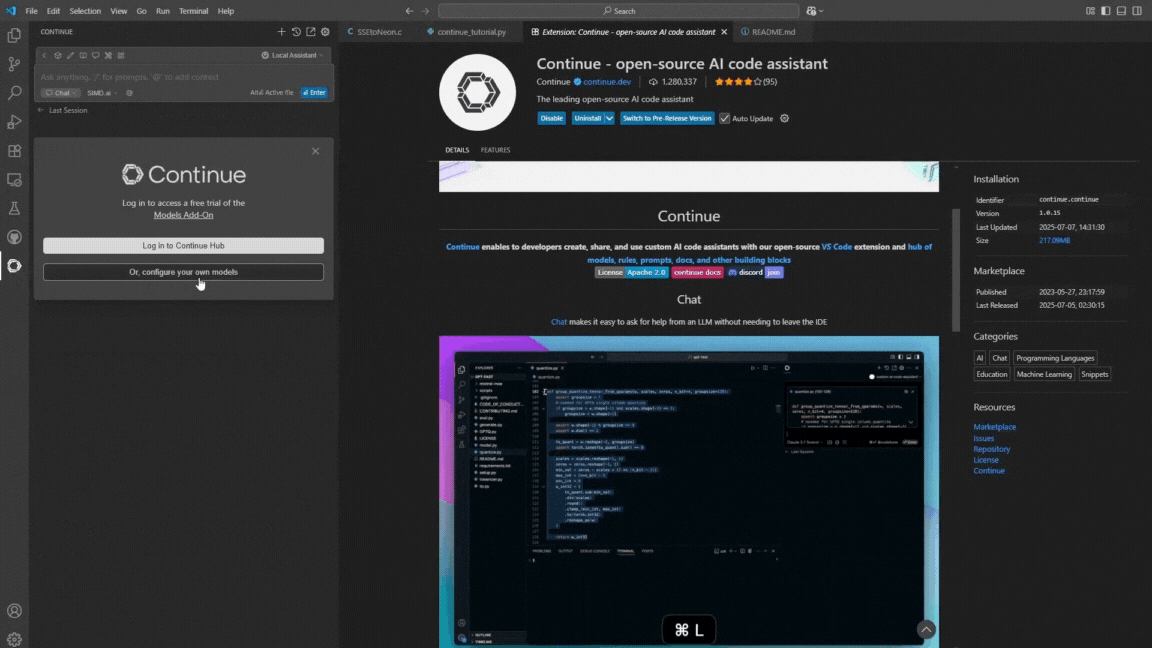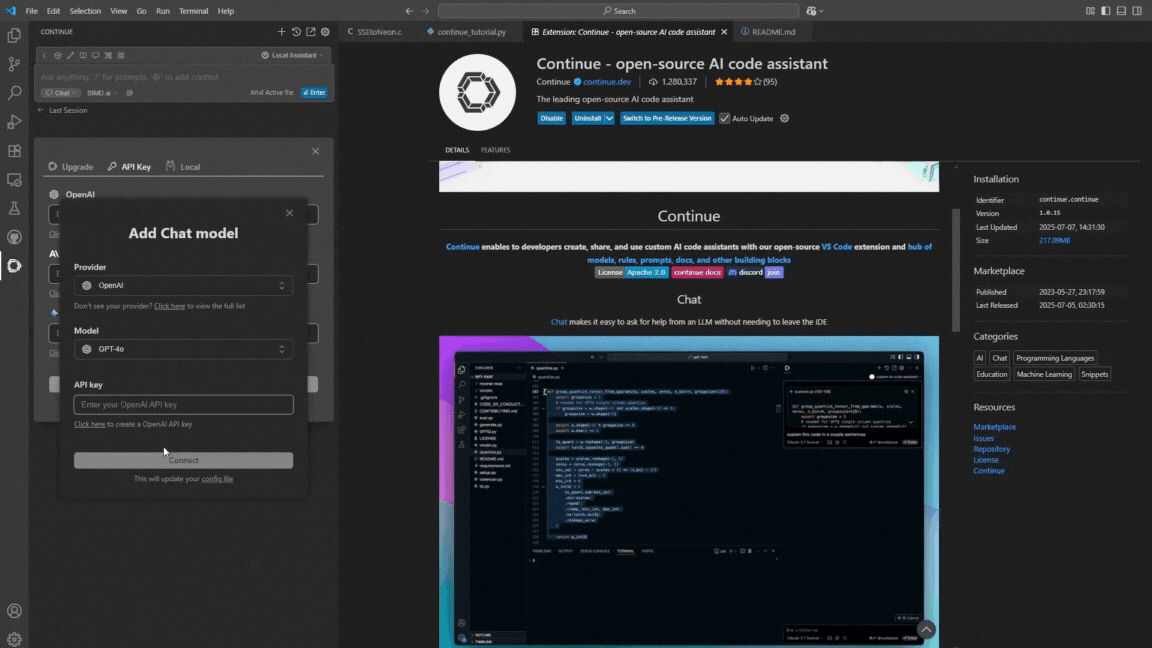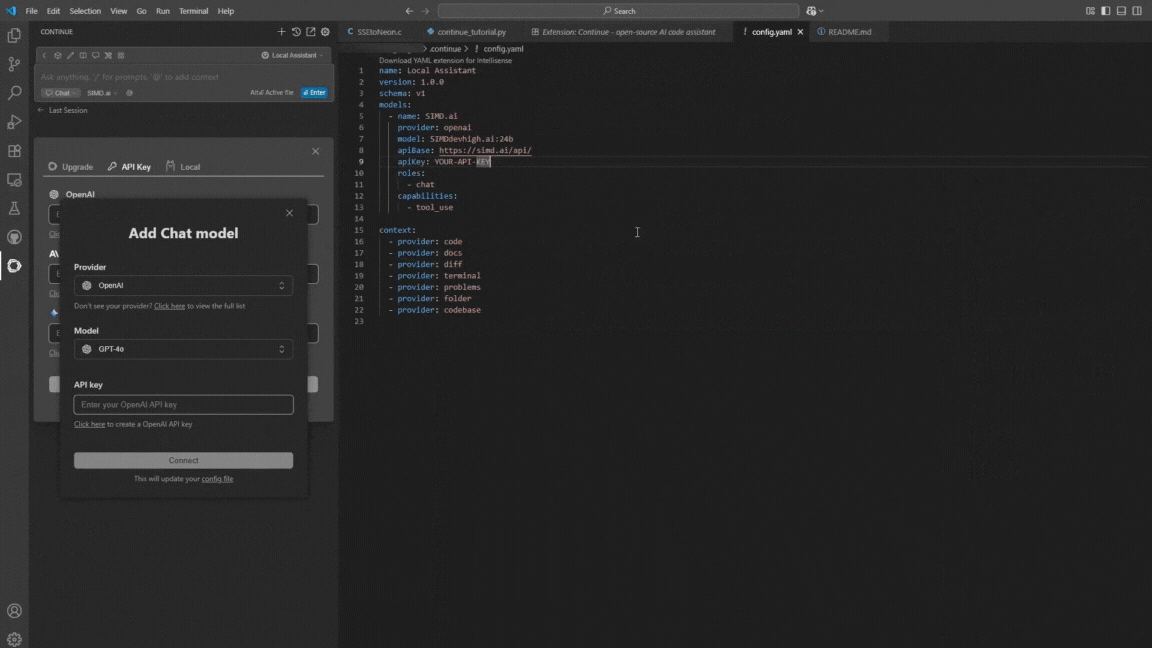
- Open Continue and select SIMD.ai from the list.
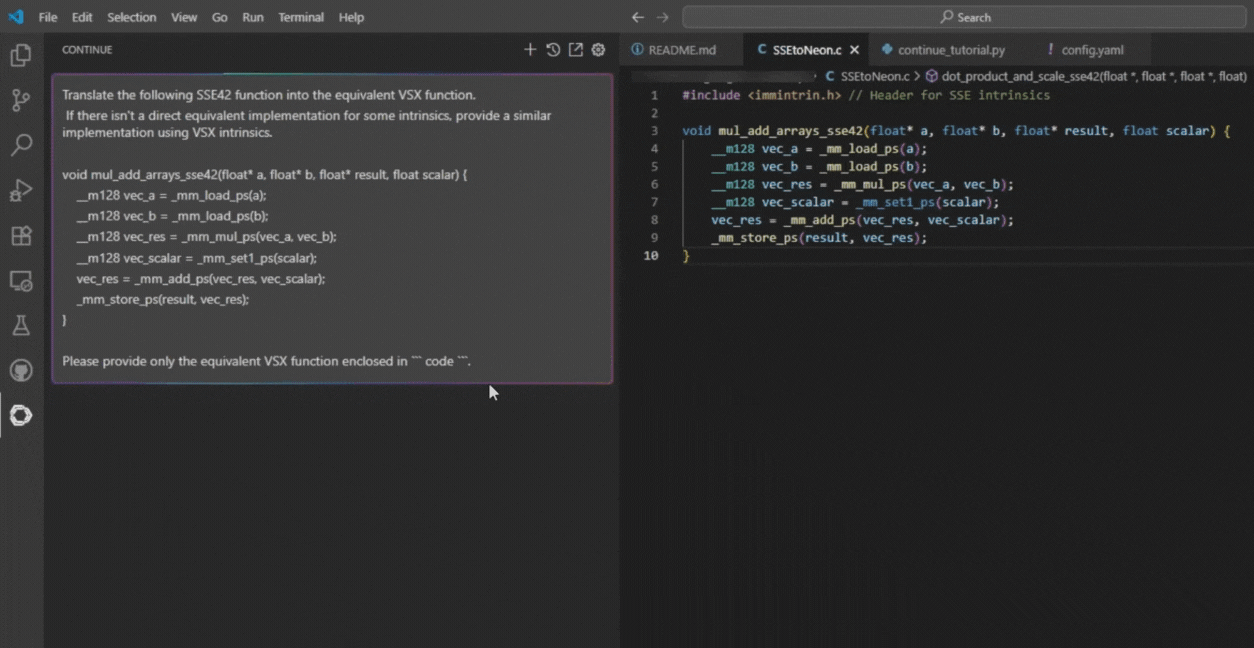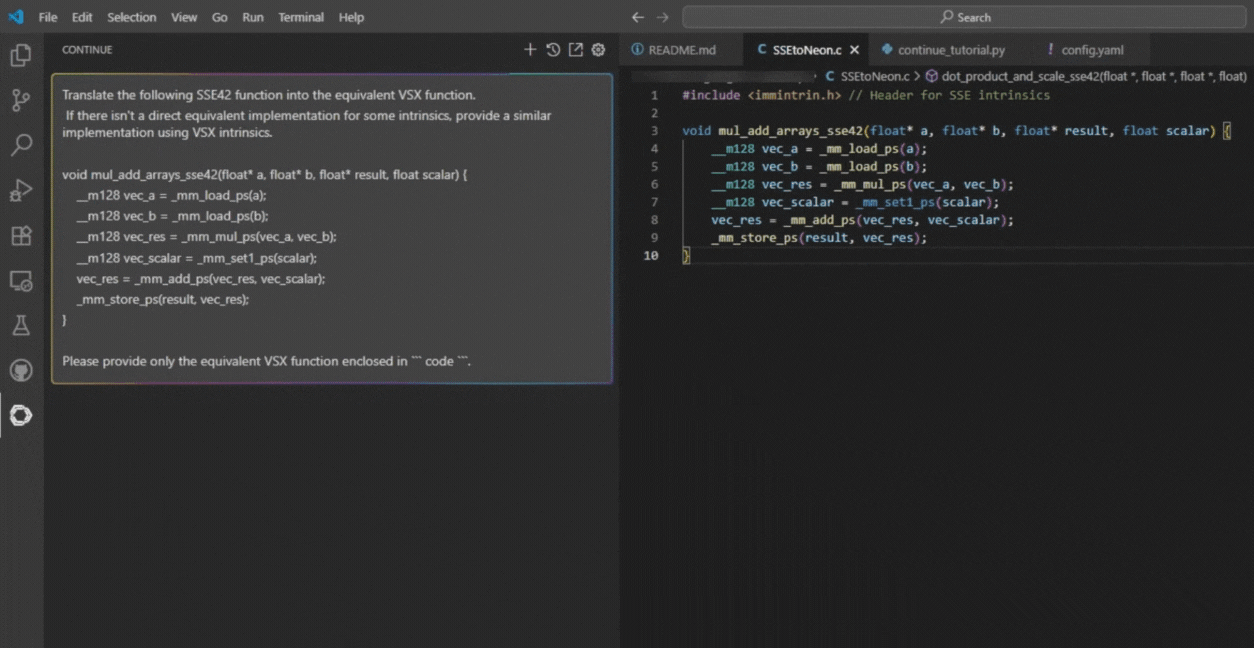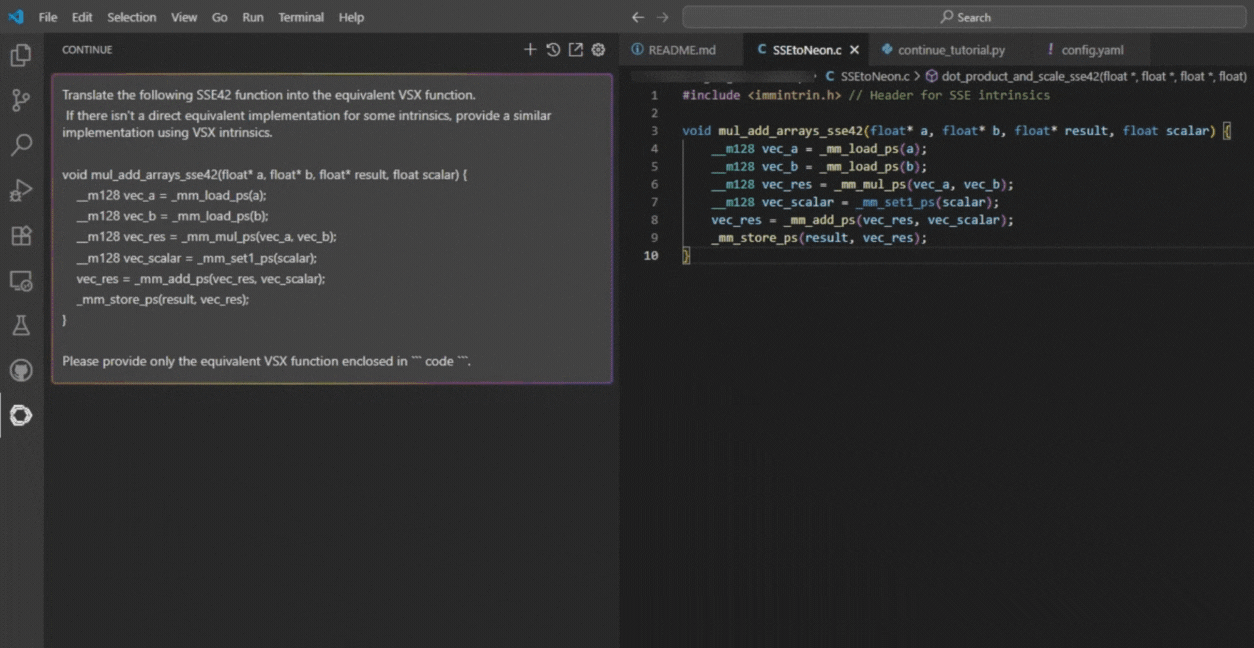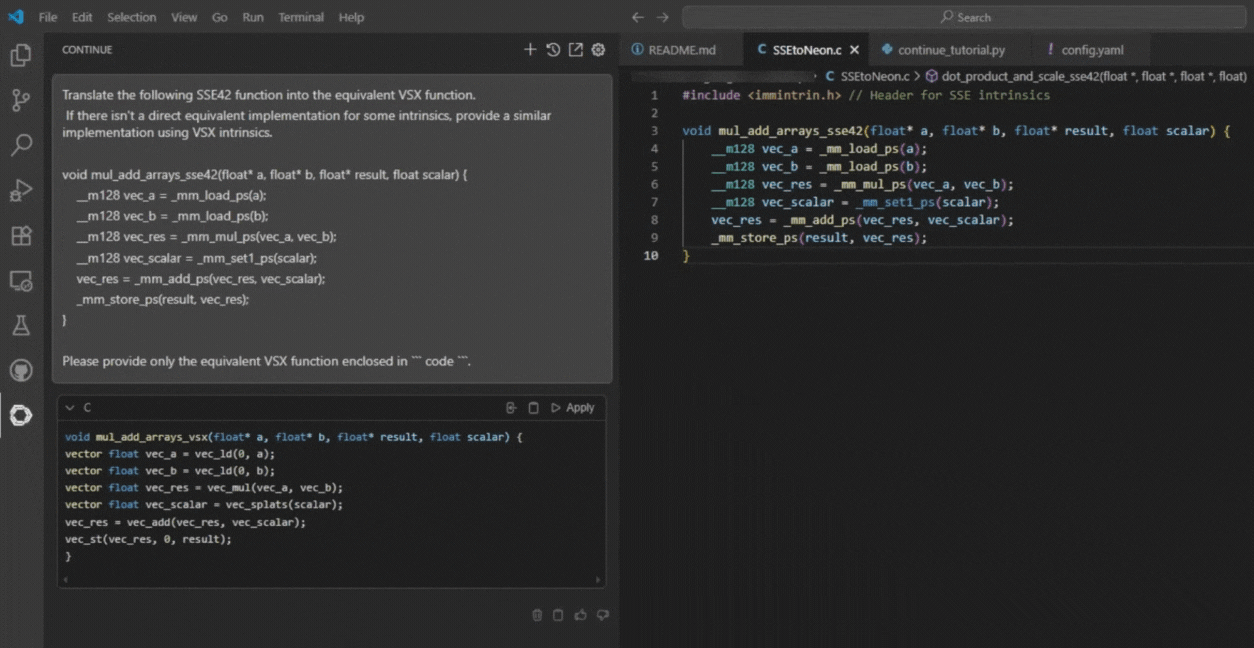
API Key & Limits
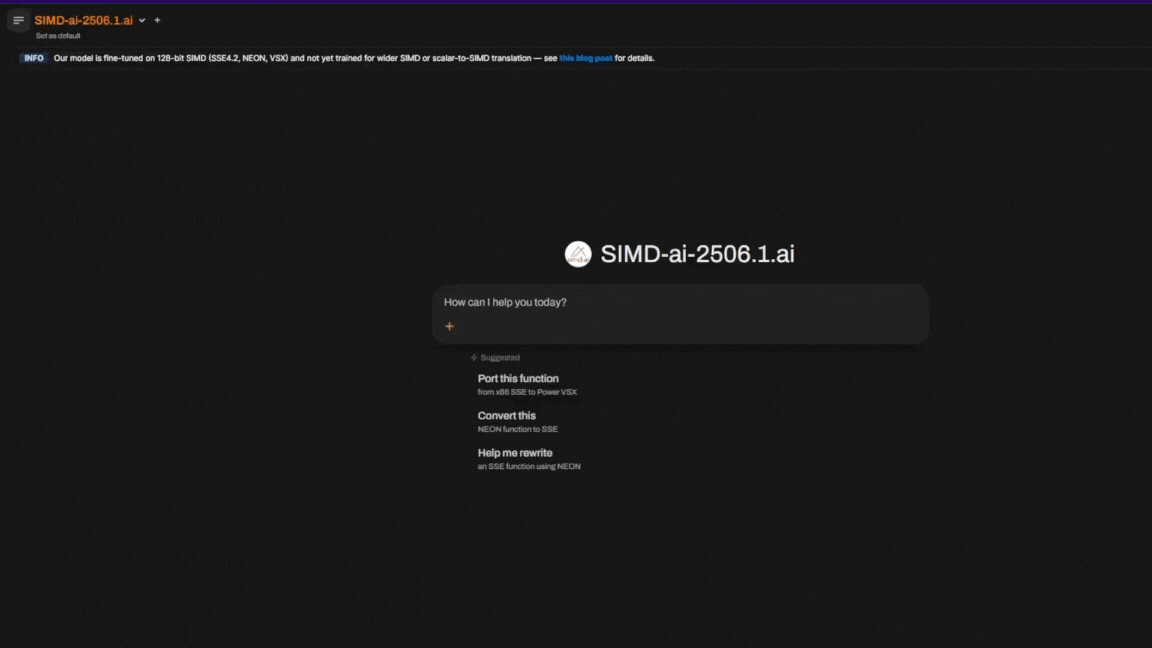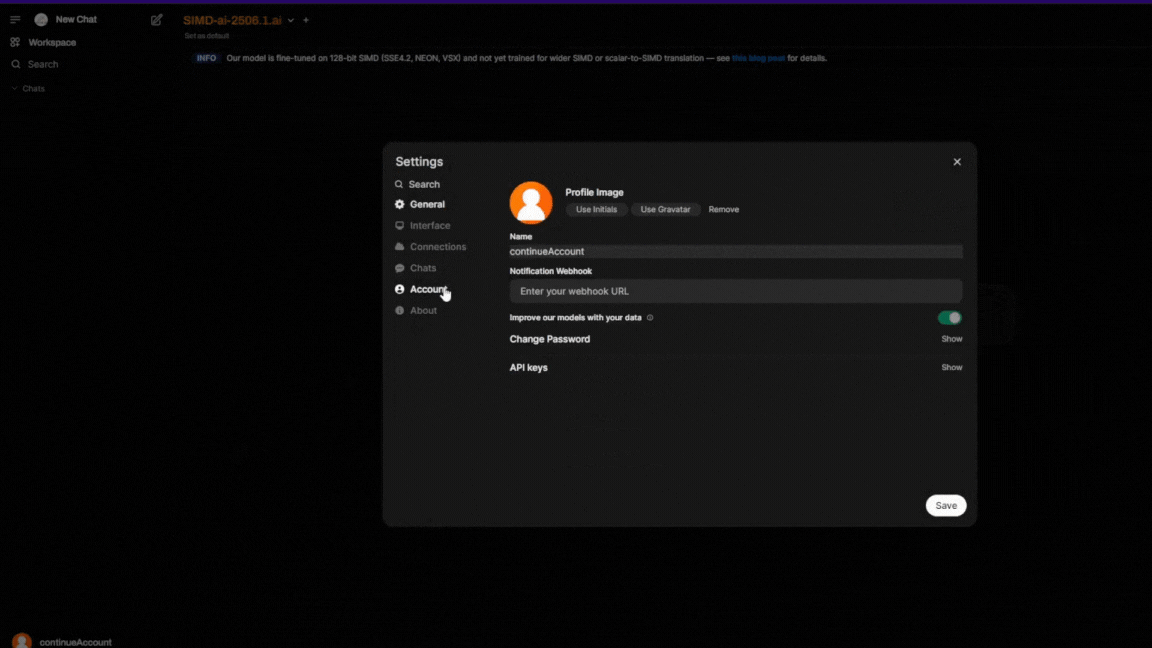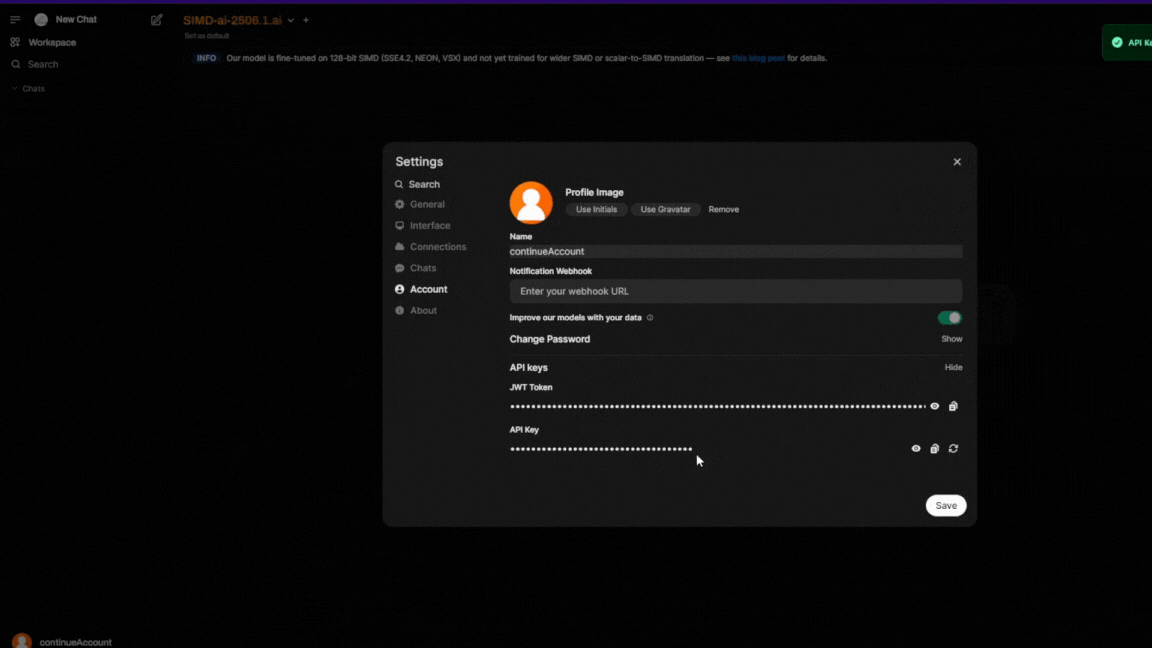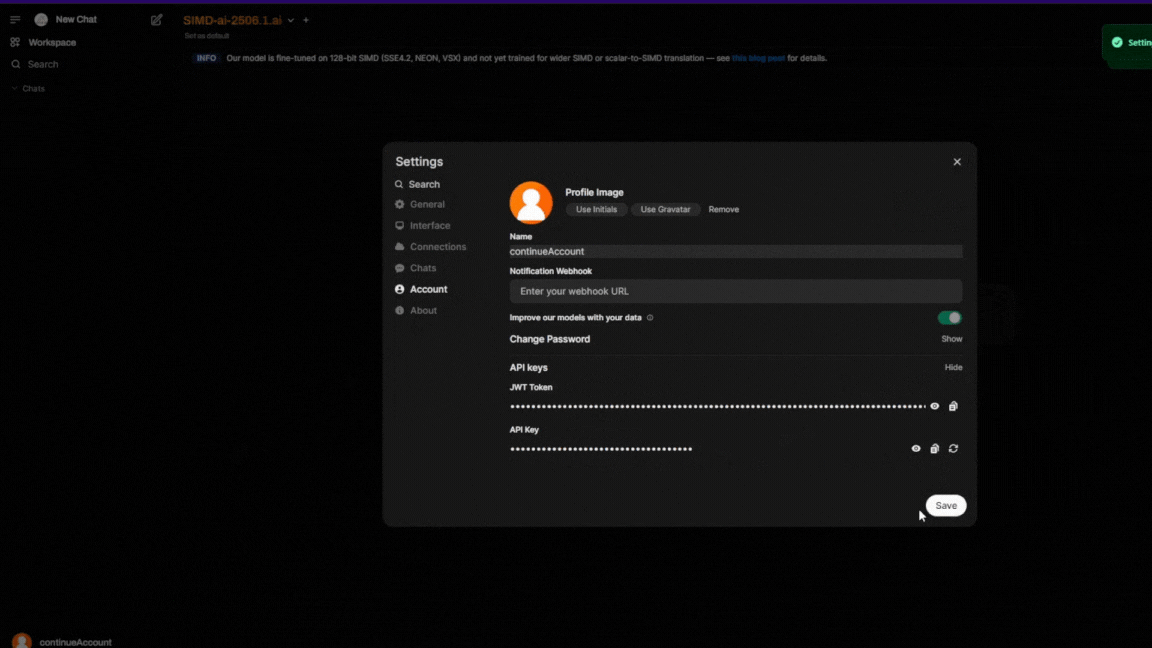
- Your API key can be created in your account settings and used directly.
- Limits and quotas depend on your own account and plan.
After completing these steps, you're running Continue with SIMD-ai-2506.1:24b model.
To sum up: for the best results, stick to the instructions and tips provided in this guide. Being clear about source and target architectures, keeping function sizes manageable, and iterating when needed will help you unlock the full potential of SIMD-ai-2506.1:24b.
Thanks for using our model! We’re eager to hear your feedback. Want to become a beta tester? Sign up at simd.ai.
SIMD Intrinsics Summary
| SIMD Engines: | 6 |
| C Intrinsics: | 10444 |
| NEON: | 4353 |
| AVX2: | 405 |
| AVX512: | 4717 |
| SSE4.2: | 598 |
| VSX: | 192 |
| IBM-Z: | 179 |
Recent Updates
November 2025- LLVM-MCA Metrics: Added latency and throughput data for each intrinsic on a per-CPU basis, plus overall plots for visual analysis.
- IBM-Z SIMD Integration: New SIMD architecture support integrated, including 179 intrinsics.
- Search Engine Migration: Switched from Elasticsearch to Meilisearch — 16× less memory usage, 100× faster responses, and improved search quality.
- Updated Statistics: Scanning expanded to more than 59k repositories, now also including IBM-Z statistics.
Previous Updates
- Intrinsics Organization: Ongoing restructuring of uncategorized intrinsics for improved accessibility.
- Enhanced Filtering: New advanced filters added to the intrinsics tree for more precise results.
- Search Validation: Improved empty search handling with better user feedback.
- Changelog Display: Recent changes now visible to users for better transparency.
- New Blog Post: "Best Practices & API Integration" guide added to the blogs section.
- Dark Theme: Added support for dark theme for improved accessibility and user experience.