Intrinsic Statistics in 13,000 GitHub Repositories - Insights and Patterns
Introduction
Intrinsics are most important at performance-critical programming, enabling developers to leverage hardware-specific instructions for speedups in computational tasks. From SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) operations to vectorized processing, intrinsics provide fine-grained control over hardware—but how widely are they used in practice?
To answer this, we conducted an extensive analysis of 13,000 GitHub repositories, focusing on the presence and usage patterns of intrinsics. This blog presents the findings, shedding light on the adoption trends, the most popular intrinsics, and the programming practices developers employ when working with them.
Here's a glimpse into what we found:
- The overall adoption rate of intrinsics in various open-source projects.
- The frequency and patterns of intrinsics used in combination.
Background
What Are Intrinsics?
Intrinsics are low-level functions that provide direct access to CPU instructions not otherwise available through high-level languages. They are commonly used for:
- SIMD Operations: Accelerating loops by processing multiple data points simultaneously.
- Hardware-Specific Optimization: Tapping into SSE4.2, AVX2, AVX512, or NEON instruction sets for performance boosts.
- Domain-Specific Applications: Powering tasks like image processing, signal analysis, and AI workloads.
Why GitHub?
GitHub hosts an enormous variety of public repositories, making it the best choice for understanding real-world coding practices. Analyzing these repositories reveals not only how developers are using intrinsics but also where they are most impactful.
Objectives of the Study
The study aimed to:
- Quantify the adoption of intrinsics across various projects.
- Identify the most frequently used intrinsics and instruction sets.
- Uncover domain-specific patterns and coding practices.
Methodology
Data Collection
To perform this study, we:
- Selected 13,000 repositories using criteria such as programming language (C, C++, Rust)
- Focused on repositories with explicit intrinsic calls and included wrapper libraries to identify which intrinsics are used within them.
Analysis Tools
We employed the following tools and techniques:
- Clang Analyzer: To extract intrinsics directly from code, ensuring accurate detection.
- Code Parsing: Extracted intrinsic usage through regular expressions and AST parsers.
- Data Processing: Aggregated results using Python and visualization libraries.
- Manual Verification: Validated findings by cross-referencing against repository metadata and commit history.
Scope
The study primarily covered:
- SIMD intrinsics: (e.g., Intel SSE4.2, Intel AVX2(includes AVX), Intel AVX512, Arm NEON,Power VSX).
- Repositories written in C, C++, and Rust.
- Public repositories available as of 2024.
Limitations
Some limitations include:
- Domain Bias: Popular domains like image processing and gaming may skew the results.
- Temporal Incompleteness: Some repositories may not reflect the latest practices.
- Prototype Variations: Certain intrinsics share the same name but differ in their function prototypes.
Results
2. Most Popular Intrinsics
The results were analyzed, and the following charts were generated.
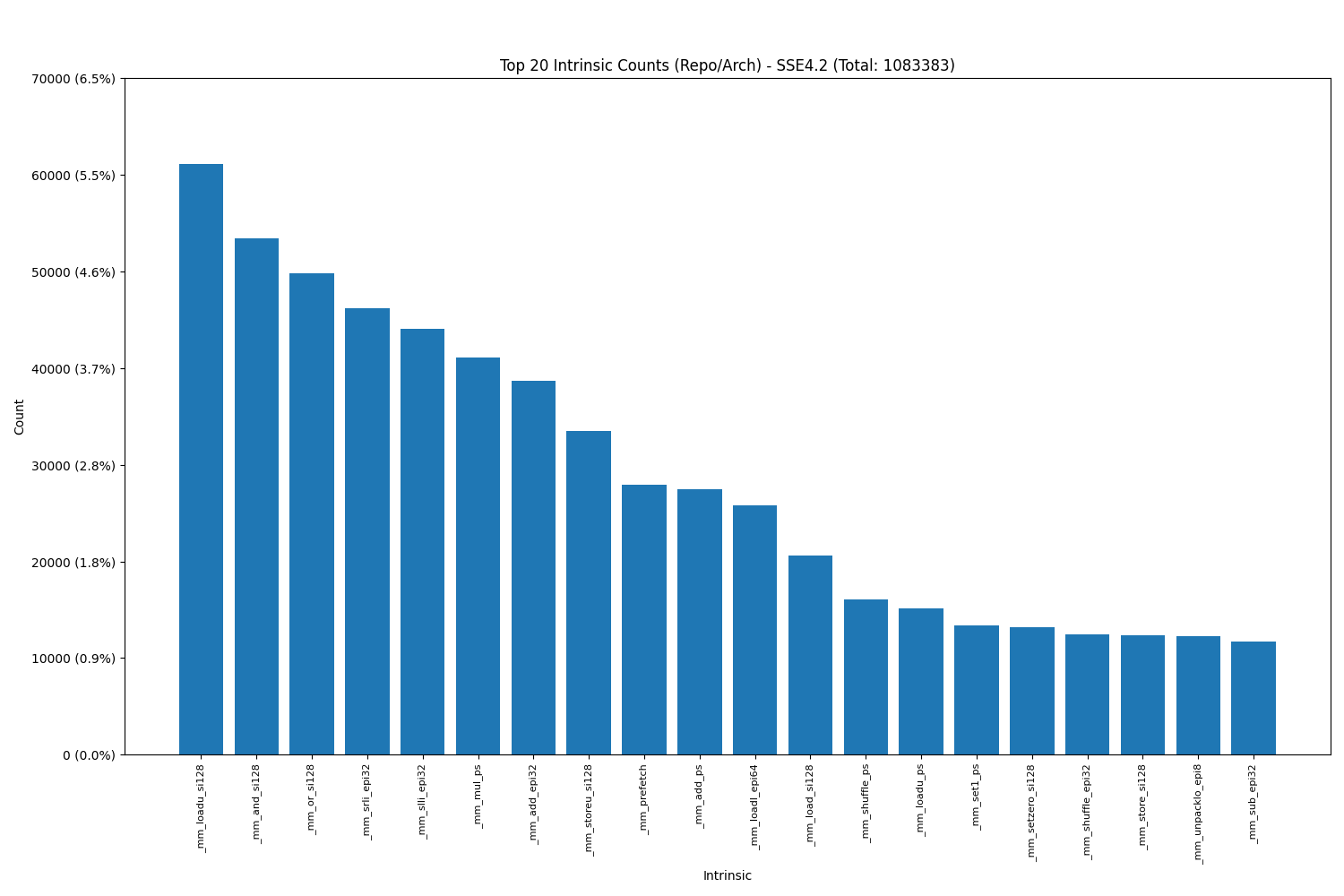
Intel SSE4.2:
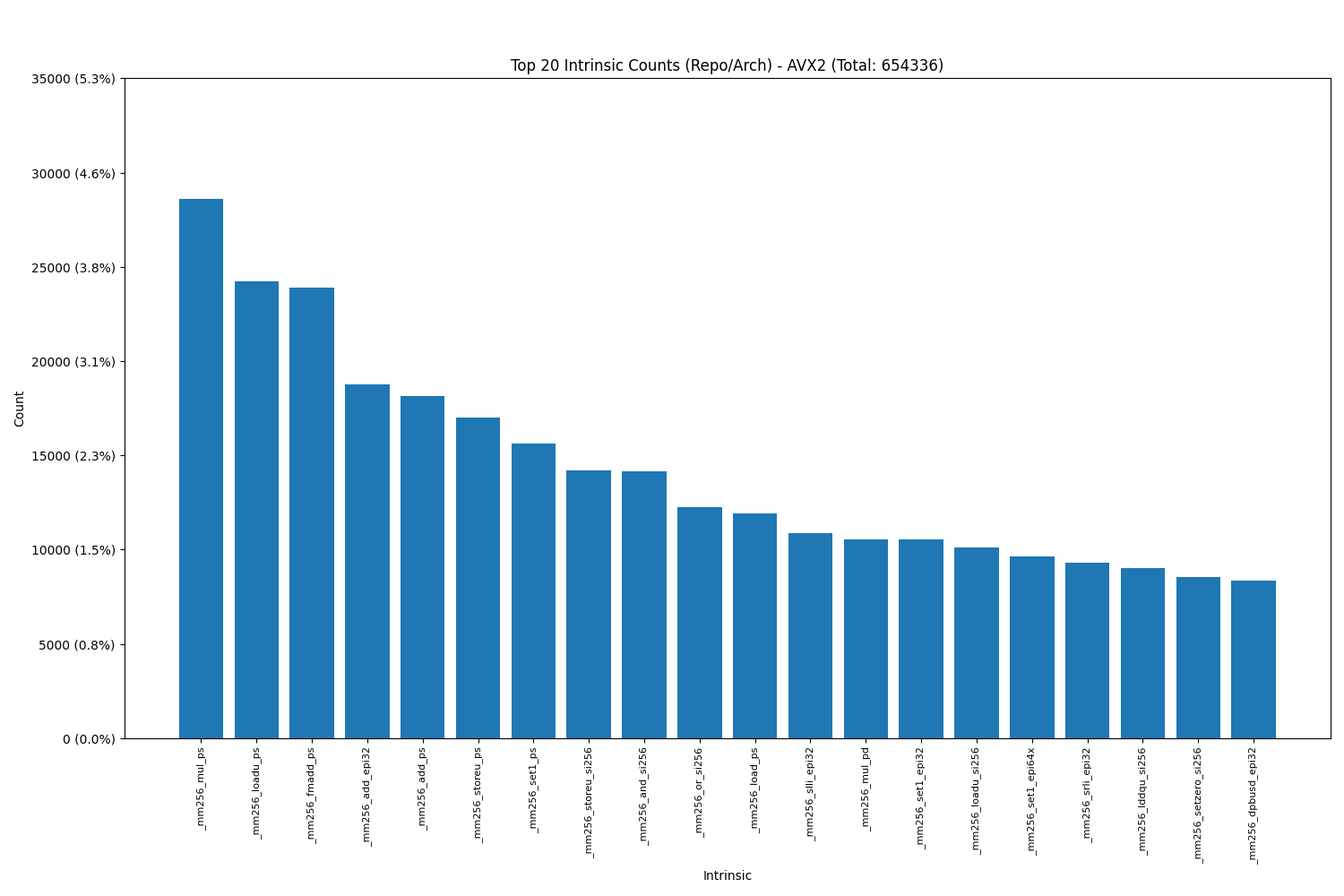
Intel AVX2(includes AVX):
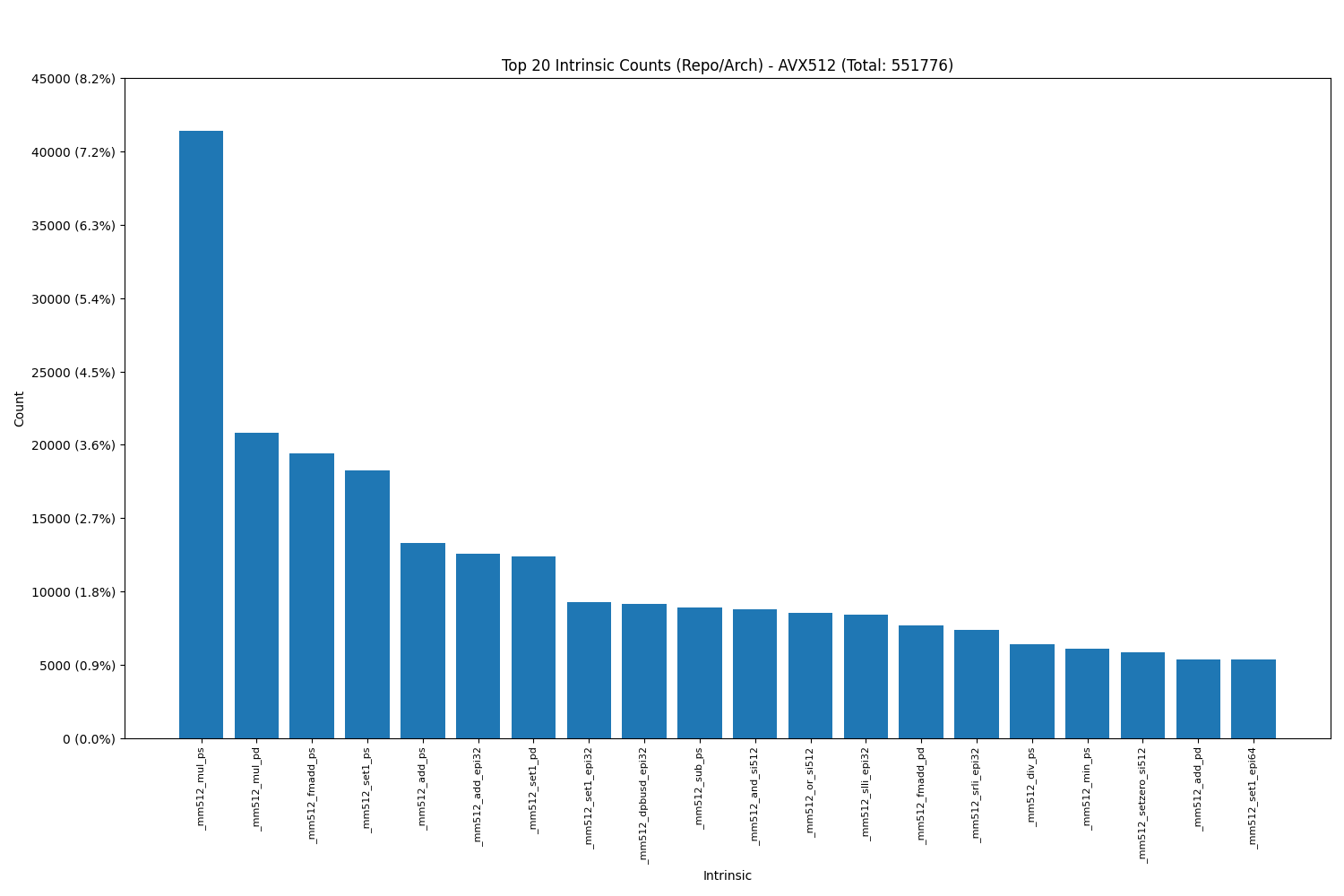
Intel AVX512:
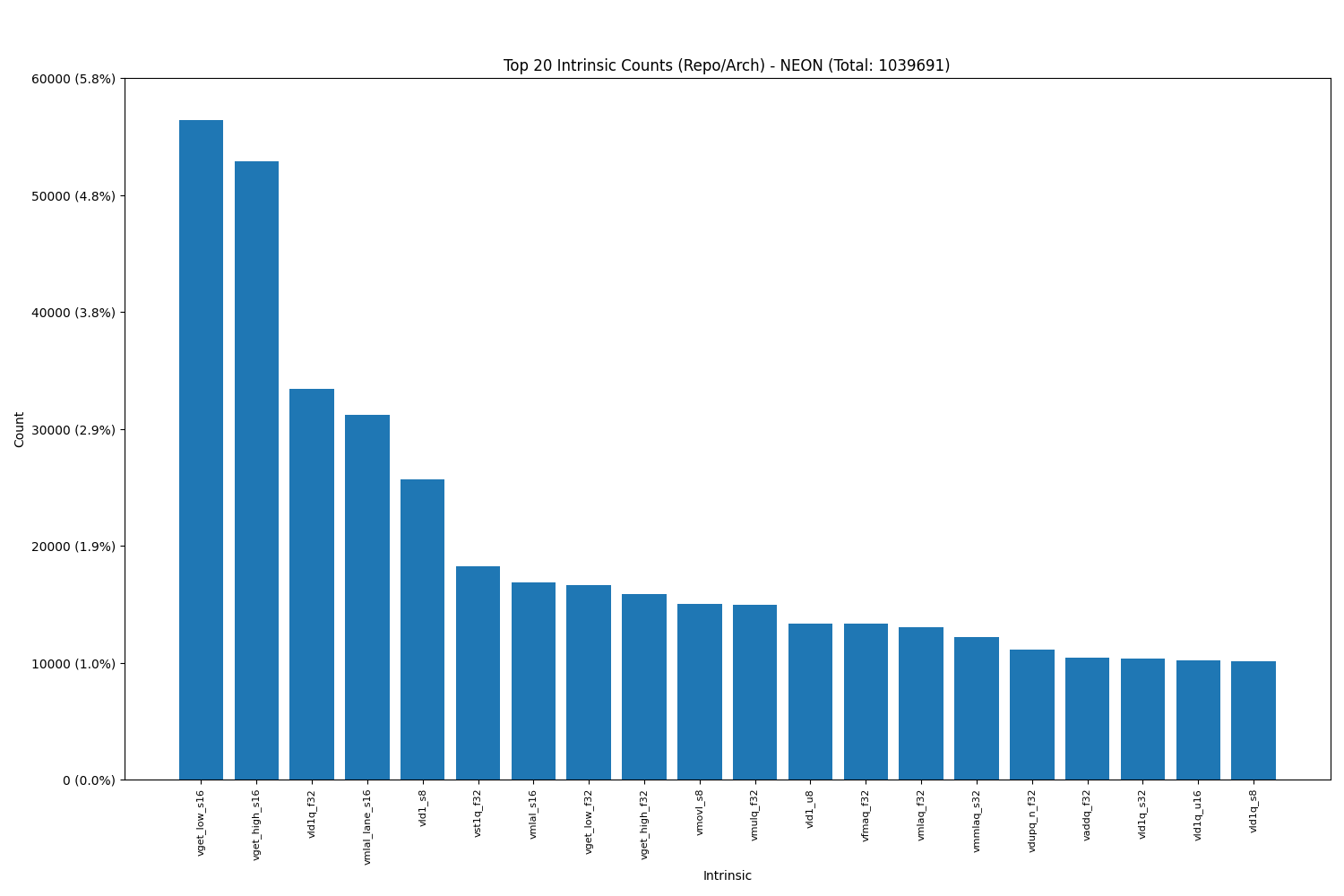
Arm NEON:
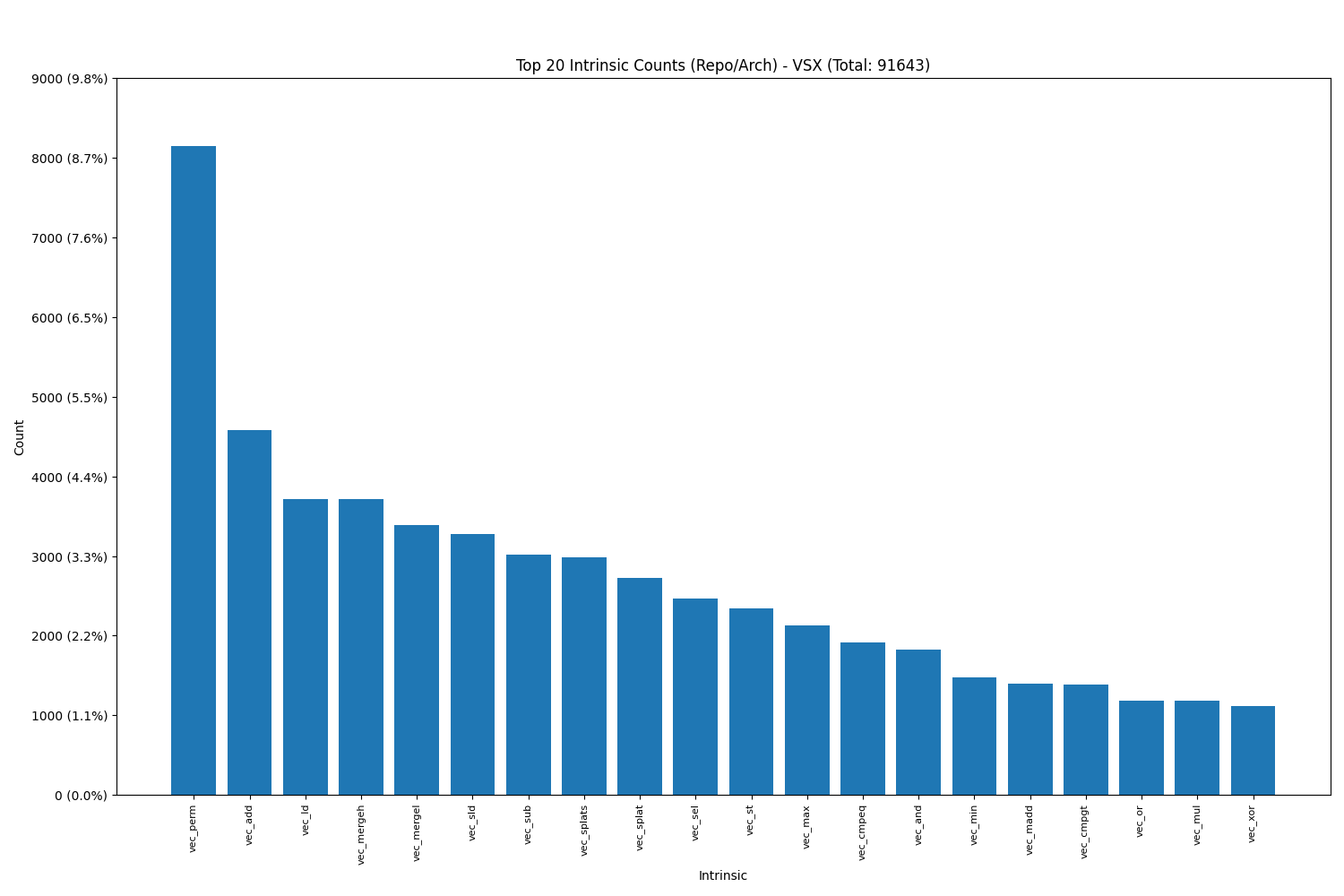
Power VSX:
3. Popular Pair and Triplets of Intrinsics
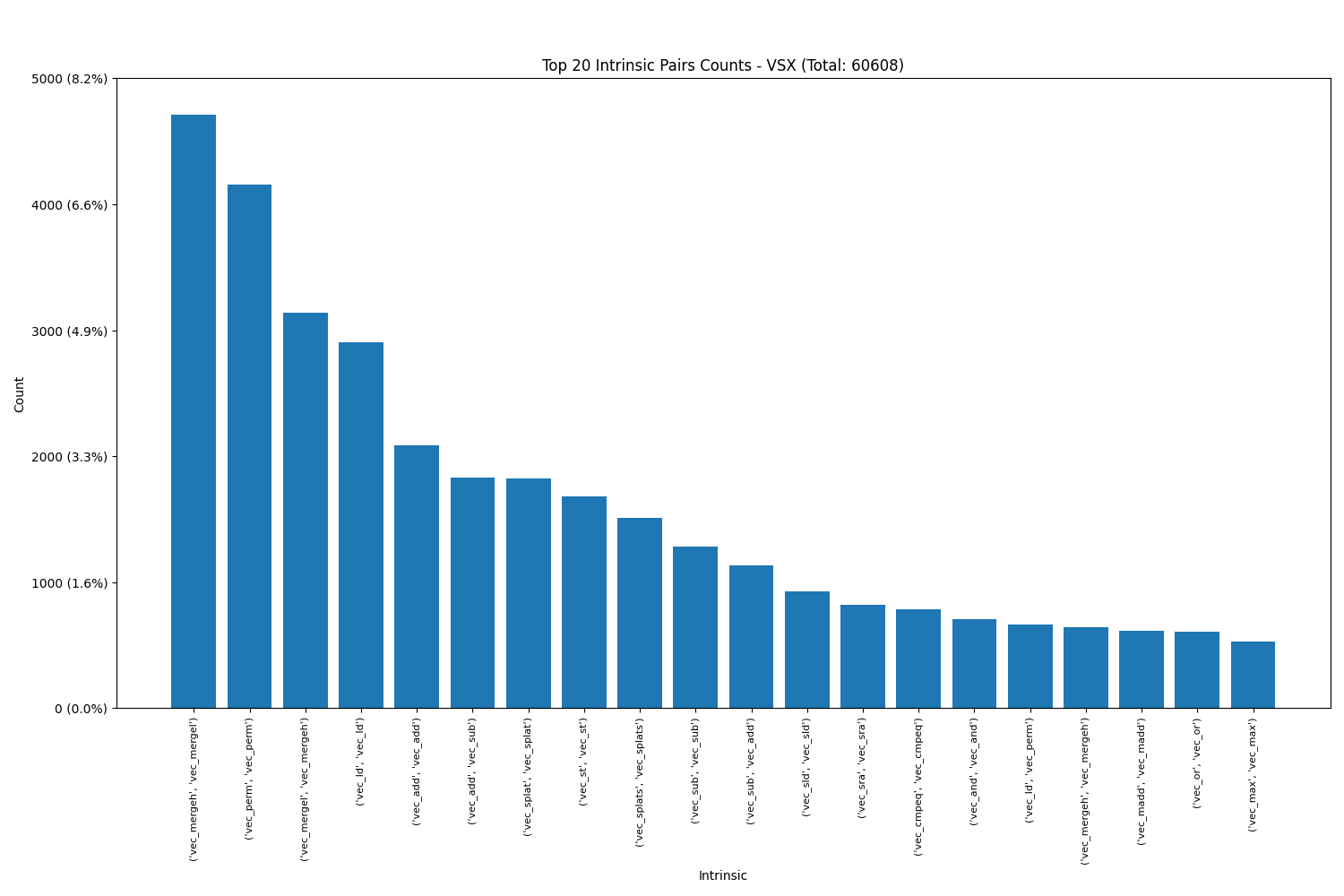
It was interesting to observe that certain pairs and triplets occurred with much higher frequency than others. Notably, in Power VSX, the most popular pair was (vec_mergeh, vec_mergel), while in ARM Neon, the pair (vld1q_f32, vld1q_f32) was the most frequently used.
Pairs:
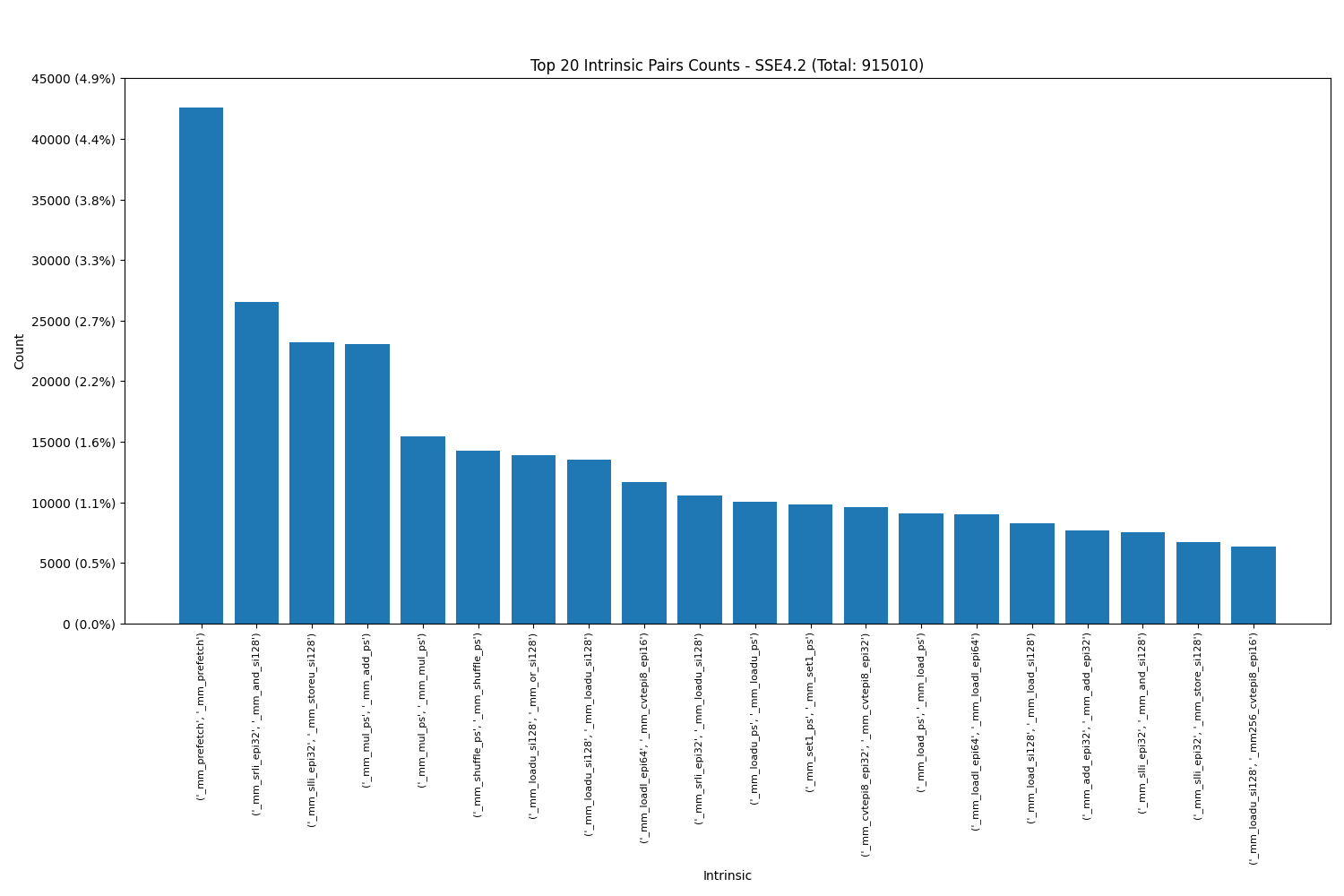
Intel SSE4.2:
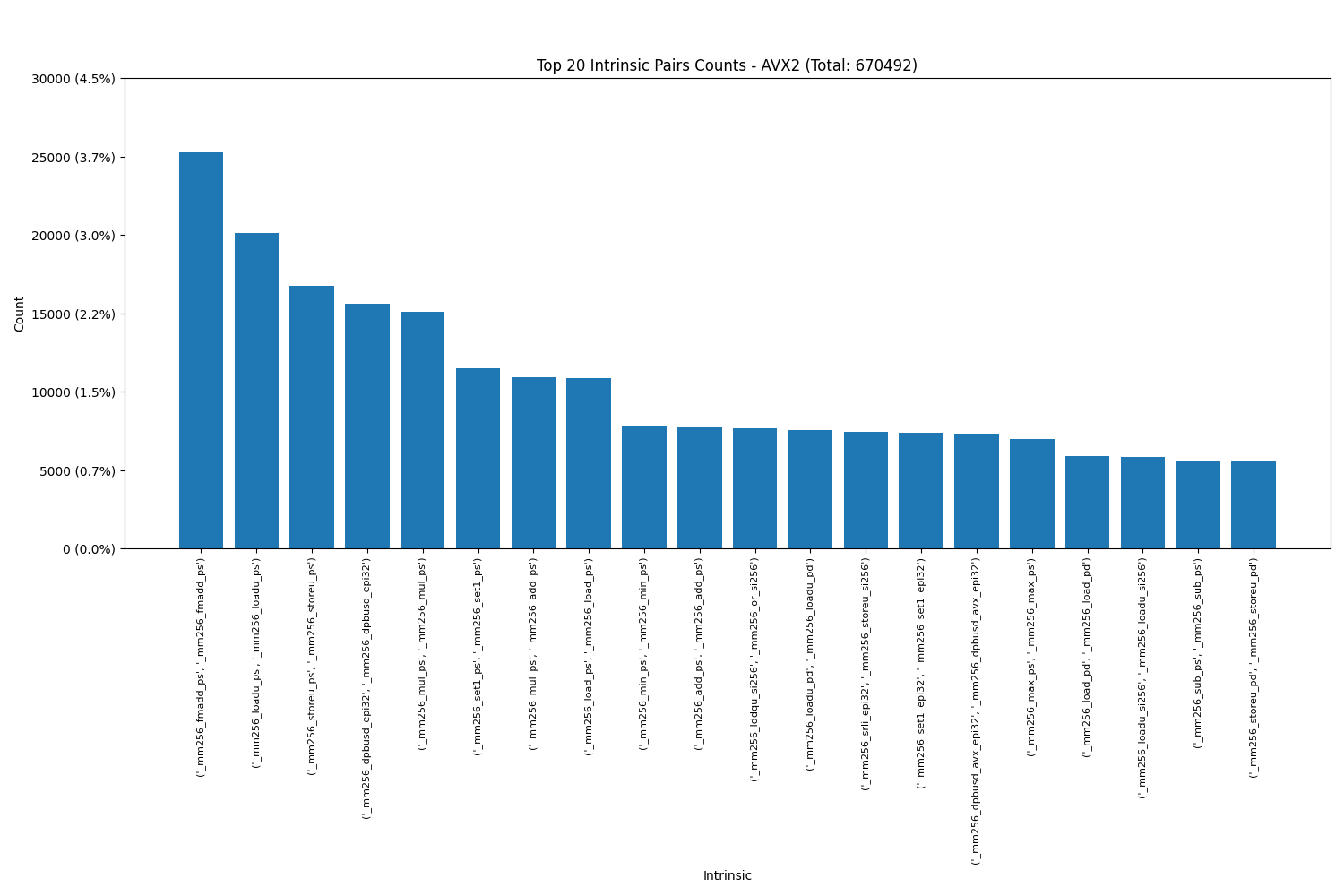
Intel AVX2(includes AVX):
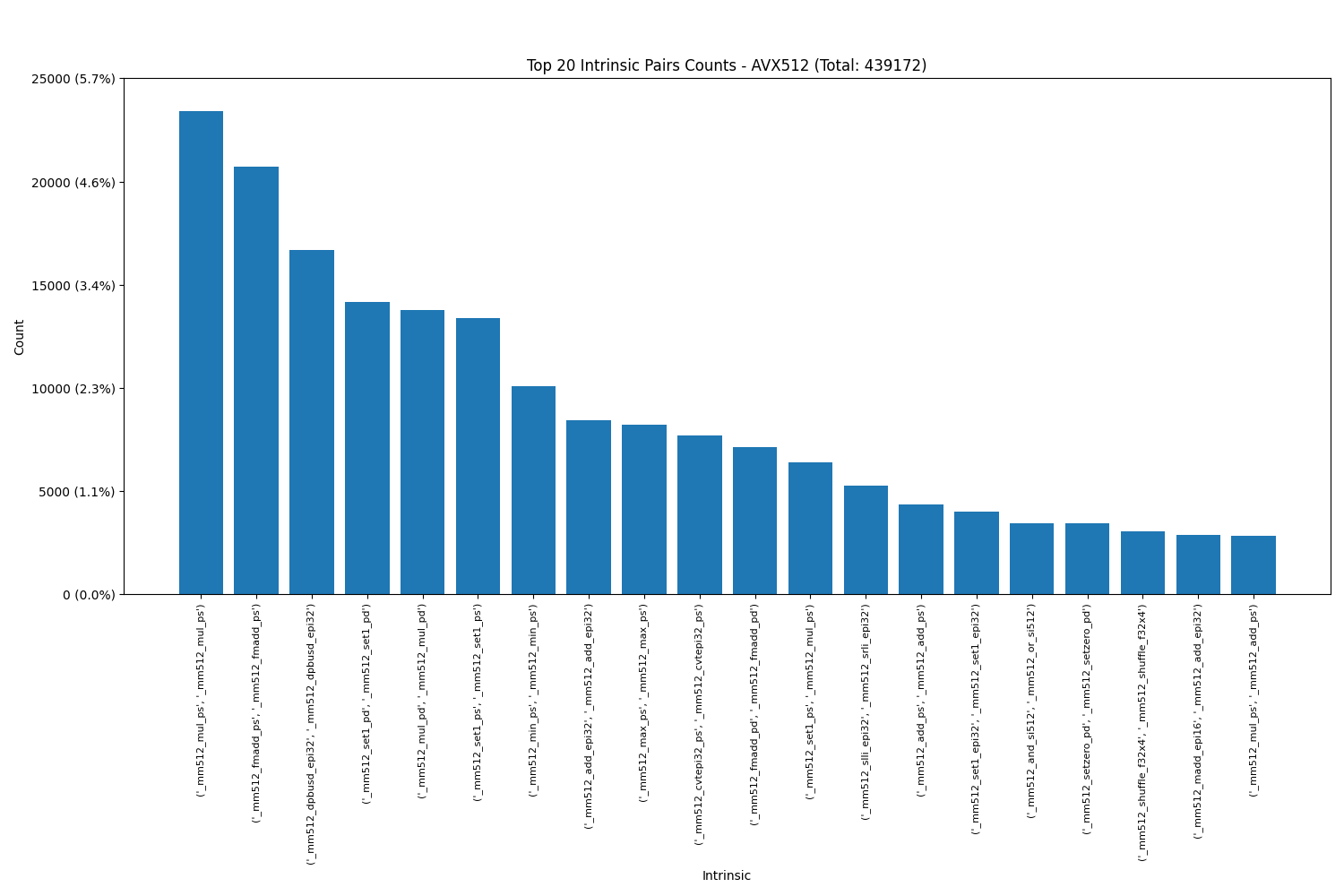
Intel AVX512:
Arm NEON:
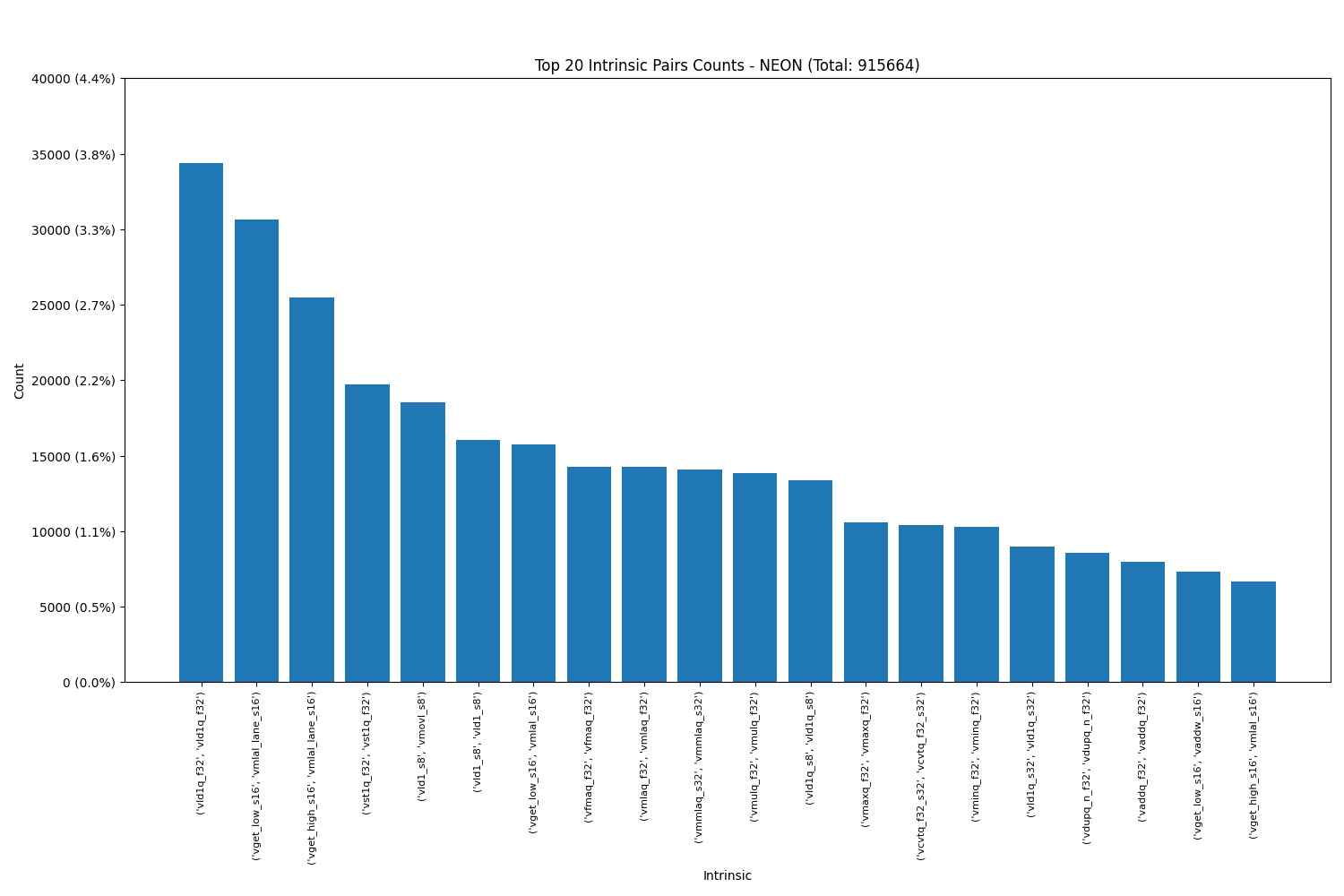
Power VSX:
Triplets: We see that each SIMD engine has their own favourite intrinsics in triplets as well.
Intel SSE4.2:
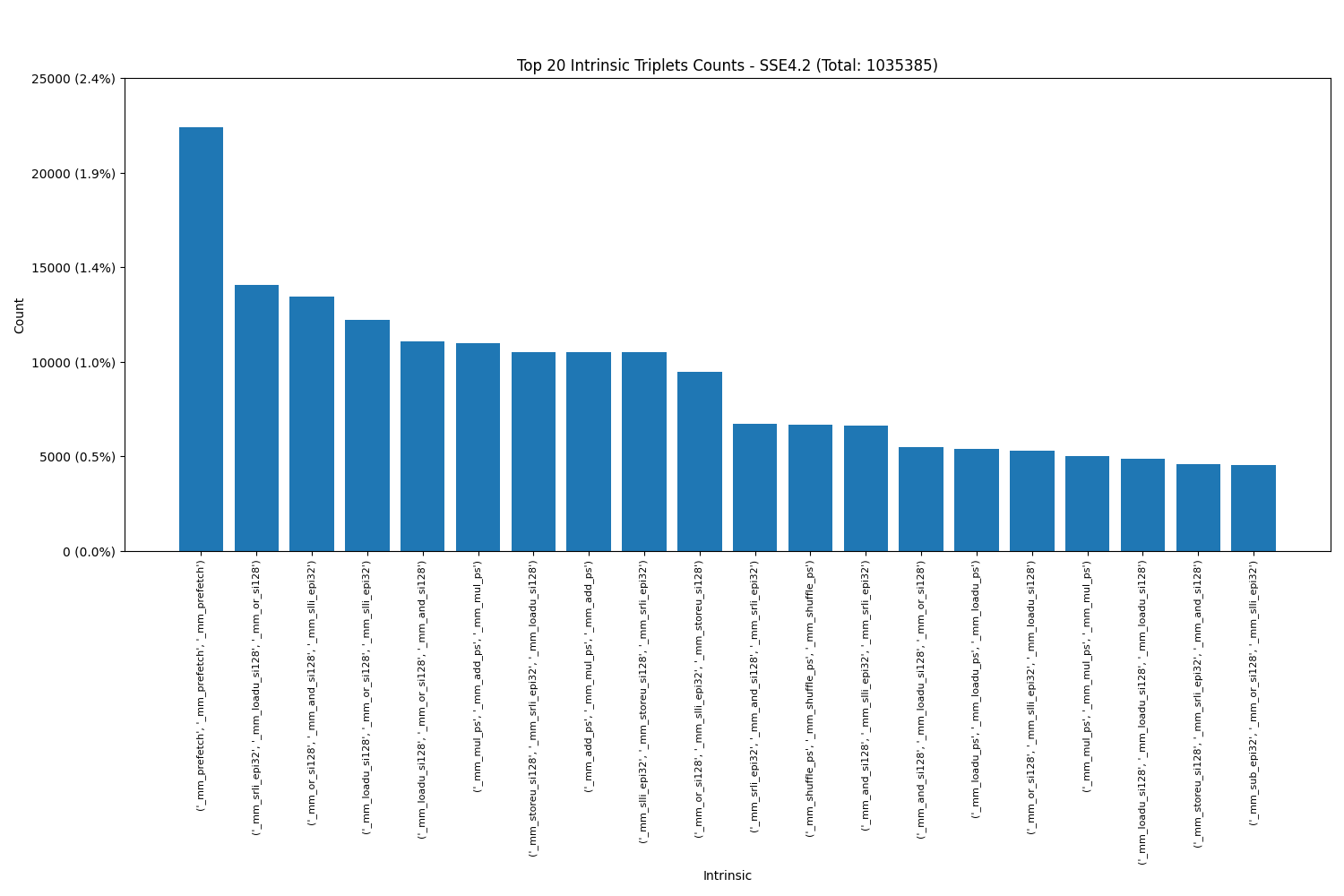
Intel AVX2(includes AVX):
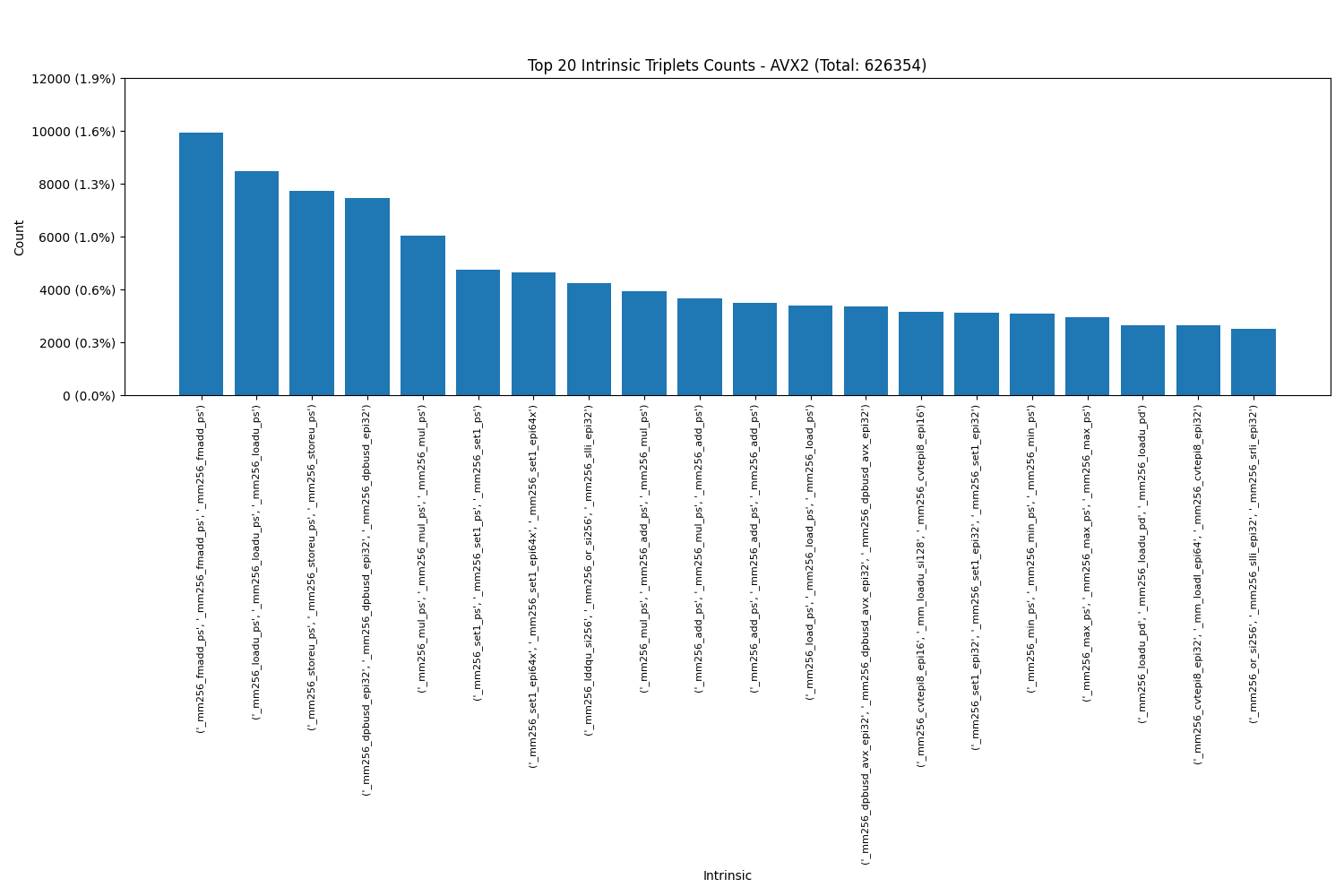
Intel AVX512:
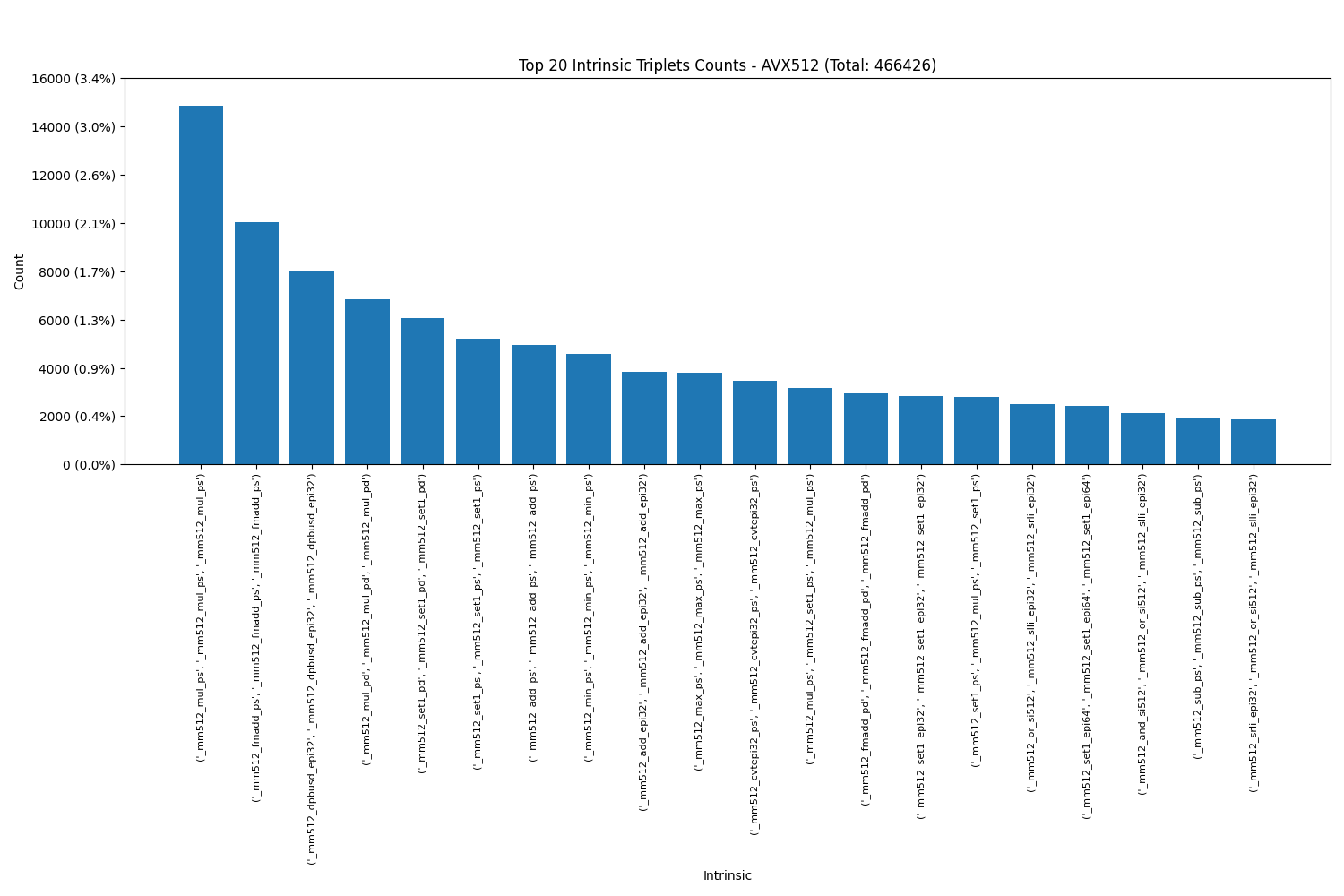
Arm NEON:
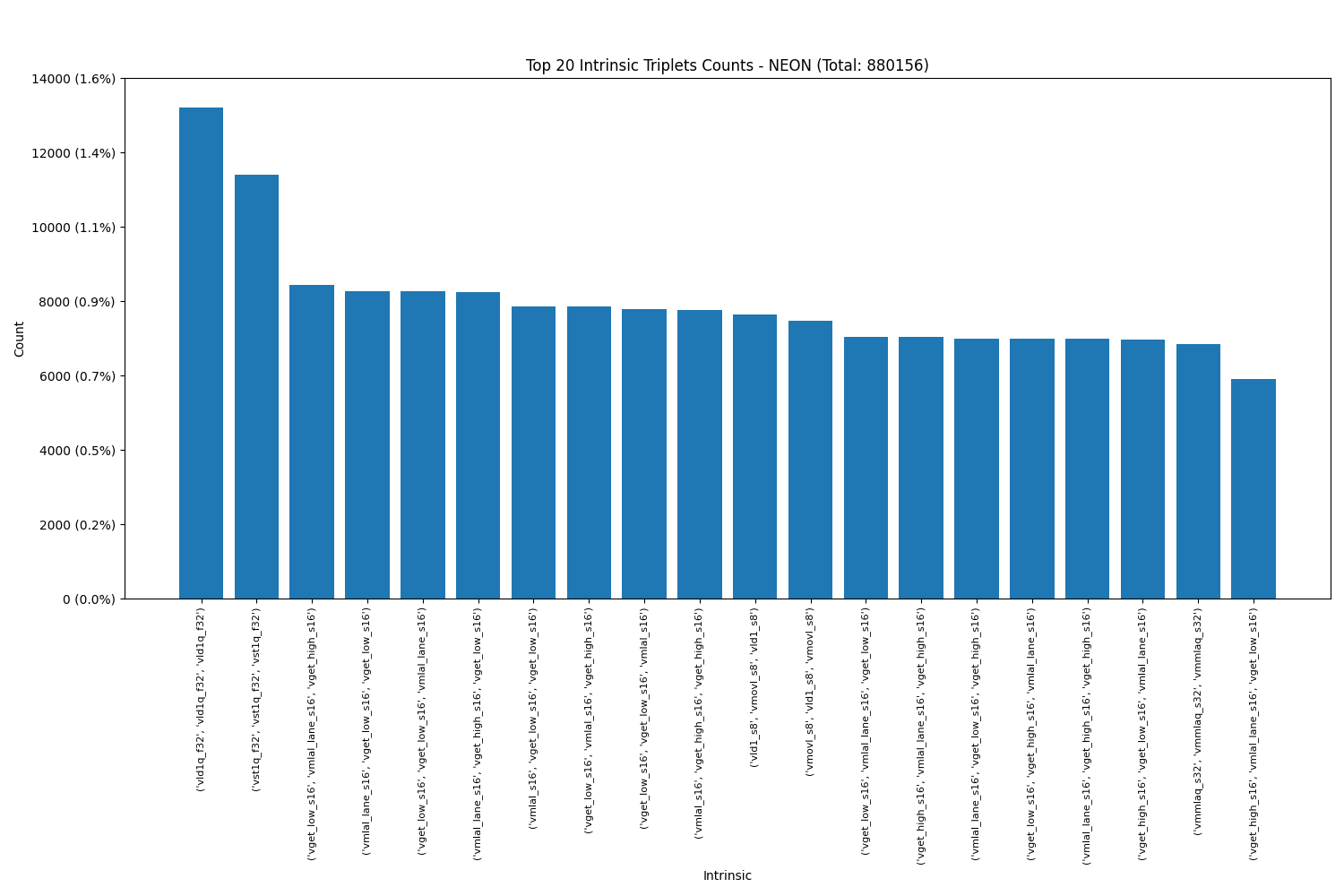
Power VSX:
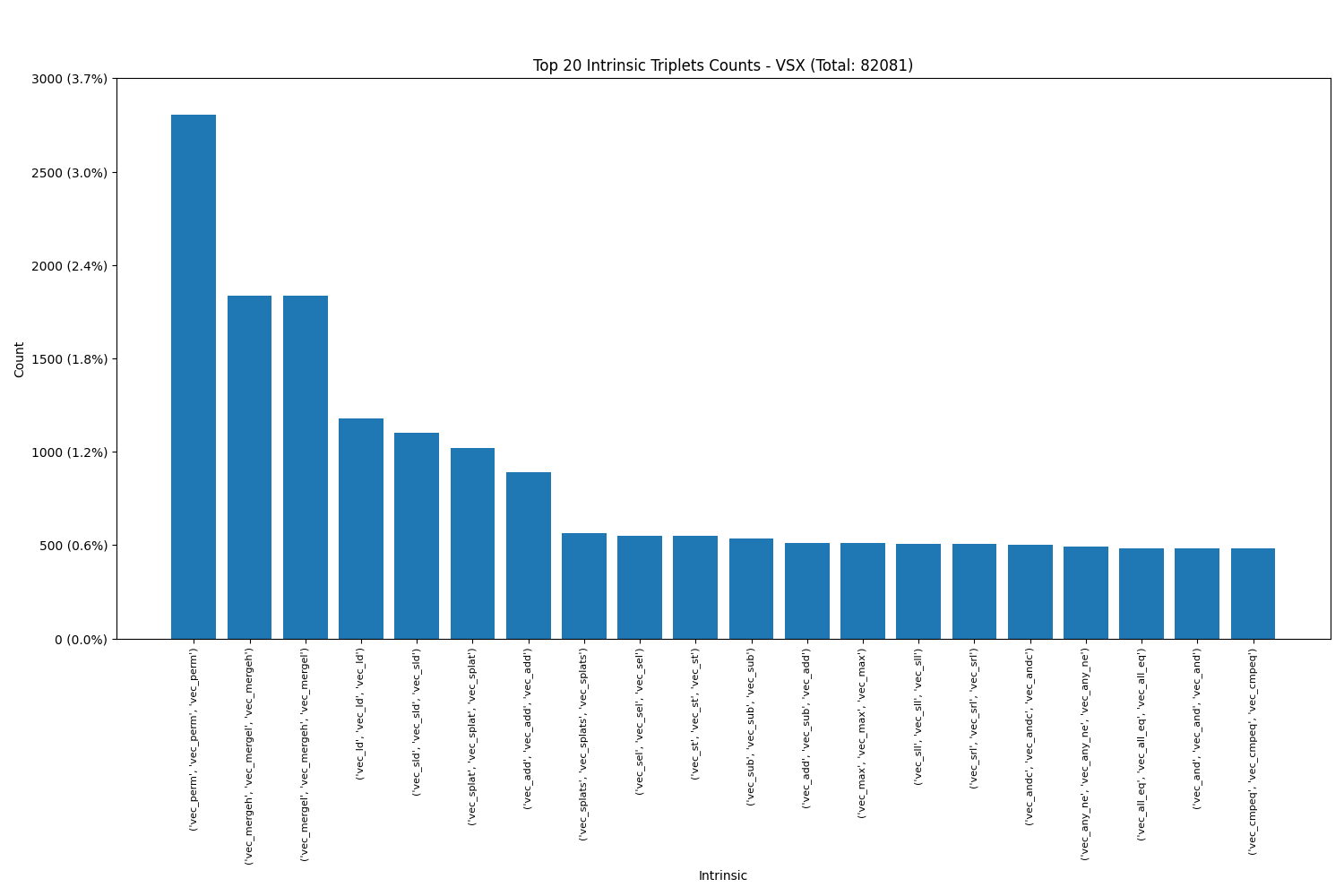
3. Least Used Intrinsics
One of the key findings is that several intrinsics exhibited extremely low usage frequency, on the order of 1/1000. This observation suggests that either users are unaware of their purpose or the intrinsics are highly specialized, limiting their applicability and potentially resulting in inefficient use of silicon space. Notably, the most unused intrinsics were found in Intel AVX-512 and Arm Neon (excluding vreinterpret*).We excluded vreinterpret* because they are solely intended for casting between different data types within compilers and do not correspond to actual assembly instructions. Additionally, some intrinsics had no matches at all, further highlighting their lack of adoption.
| Architecture | Lower matches than 10 (0.001%) |
|---|---|
| Intel SSE4.2 | 1 |
| Intel AVX2(includes AVX) | 6 |
| Intel AVX512 | 849 |
| Arm Neon | 407 |
| Power VSX | 10 |
Discussion
Key Takeaways
- The data shows that load intrinsics, as expected, are the most commonly used, highlighting their essential role in memory operations and overall performance optimization.
- Several intrinsics, particularly those with very low usage frequencies, are either rarely needed or highly specialized, suggesting limited applicability in general use cases.
- The data reveals a clear preference for certain intrinsics, while others, including those with very low adoption rates, appear to be underutilized.
- Some pairs and triplets of intrinsics show a recurring pattern, suggesting an opportunity for new intrinsics that execute the combined operation, resulting in further optimizations.
Implications
- For Developers: Many developers are unfamiliar with all available intrinsics and often struggle to find comprehensive examples. Providing more accessible documentation and use cases could help in promoting their effective use.
- For CPU Designers: CPU Designers could optimize intrinsic instruction pairs and triplets that are used too frequently in the next CPU revision by placing their circuits closer together or reducing the number of cycles required to execute them.
- Compiler Engineers: By identifying specific code paths—such as pairs or triplets of instructions—that frequently occur in programs utilizing intrinsics, and recognizing faster implementations, compiler engineers could optimize the generated code by substituting these sequences with more efficient alternatives. Furthermore, in a future revision of the processor, if an instruction is introduced to implement the operation of a frequently used pair or triplet, the compiler could recognize and replace the original sequence with the new, more efficient instruction.
Open Questions
- To what extent are certain intrinsics underutilized and can this be attributed to their impracticality/lack of usefulness?
- Is there a need to develop new intrinsics based on the frequently observed combinations of pairs and triplets identified in the analysis?
Future Work
The current analysis focused on commonly used architectures like Intel SSE4.2, Intel AVX2, Intel AVX512, Arm NEON, and Power VSX. In future iterations, we plan to extend the scope to:
- Additional architectures such as RISC-V RVV 1.0, MIPS MSA, Loongson LSX/LASX, IBM Z Vector, ARM SVE/SVE2 and other emerging SIMD and Vector engines.
- Deeper exploration of underutilized intrinsics to assess their potential relevance or inefficiencies.
- Making the script more optimized and automatic to handle large-scale repository analysis with improved parallelization and error handling.
- Matrix Extensions like Intel AMX, Arm SME, Power MMA.
References
- SIMD.info: https://simd.info
SIMD Intrinsics Summary
| SIMD Engines: | 6 |
| C Intrinsics: | 10444 |
| NEON: | 4353 |
| AVX2: | 405 |
| AVX512: | 4717 |
| SSE4.2: | 598 |
| VSX: | 192 |
| IBM-Z: | 179 |
Recent Updates
November 2025- LLVM-MCA Metrics: Added latency and throughput data for each intrinsic on a per-CPU basis, plus overall plots for visual analysis.
- IBM-Z SIMD Integration: New SIMD architecture support integrated, including 179 intrinsics.
- Search Engine Migration: Switched from Elasticsearch to Meilisearch — 16× less memory usage, 100× faster responses, and improved search quality.
- Updated Statistics: Scanning expanded to more than 59k repositories, now also including IBM-Z statistics.
Previous Updates
- Intrinsics Organization: Ongoing restructuring of uncategorized intrinsics for improved accessibility.
- Enhanced Filtering: New advanced filters added to the intrinsics tree for more precise results.
- Search Validation: Improved empty search handling with better user feedback.
- Changelog Display: Recent changes now visible to users for better transparency.
- New Blog Post: "Best Practices & API Integration" guide added to the blogs section.
- Dark Theme: Added support for dark theme for improved accessibility and user experience.